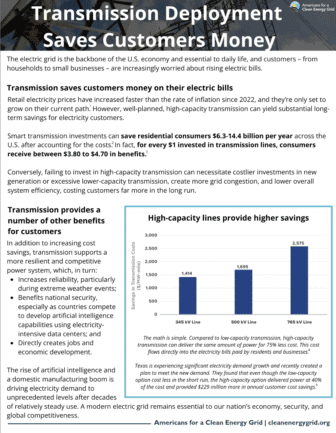
Summary Washington, D.C. — The electric grid is the backbone of the U.S. economy and essential to daily life, and customers – from households to small businesses – are increasingly […]
Today, Americans for a Clean Energy Grid (ACEG) and Grid Strategies released the report “Large-Scale Transmission Deployment Saves Consumers Money.”
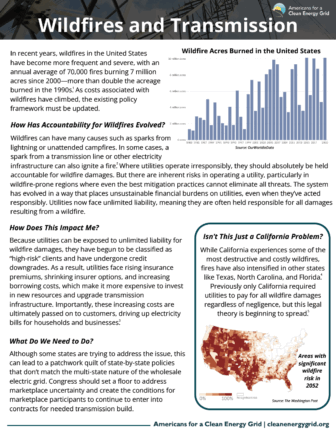
Summary Washington, D.C. — In recent years, wildfires in the United States have become more frequent and severe, with an annual average of 70,000 fires burning 7 million acres since […]
Today, Americans for a Clean Energy Grid (ACEG) and Grid Strategies released the report “Resource Adequacy Value of Interregional Transmission.”
Today, Americans for a Clean Energy Grid (ACEG) and Grid Strategies released the report “The PACE of Trust: A Framework by Community Voices for Advancing Transmission.”
Summary Washington, D.C. — Expanding the transmission grid quickly to meet growing demand requires not just technical expertise, but also strategic community engagement. Without broad community support, a transmission project […]
Today, Americans for a Clean Energy Grid (ACEG) and Grid Strategies released the report “2024 State of Regional Transmission Planning.” The report details how each transmission planning region has held up on planning since ACEG's report card in 2023.
Summary Washington, D.C. — Transmission lines are crucial for moving electricity from power plants to where it’s used. They ensure that electricity—an essential service—remains affordable, reliable, and resilient. However, the […]
Today, Americans for a Clean Energy Grid (ACEG) and Grid Strategies released the report “State Policies to Advance Transmission Modernization and Expansion.” The report delves into how state policies can drive the high-capacity, interstate transmission solutions we need.
Summary Washington, D.C. — Construction of new electric transmission lines has slowed to a trickle, from an average of 1,700 miles of new high-voltage transmission miles installed per year in […]