Transmission is the backbone of our electric system and the foundation for our country’s growth and security. Expanding and upgrading the electric transmission network will strengthen America’s economy, spur the development and use of clean and renewable energy sources, and ensure a secure and modern power system.
The electric transmission system is a marvel of modern engineering that has powered our growth for over half a century. Today, the aging grid is less reliable and less capable of meeting our 21st Century needs for abundant, inexpensive and domestic clean energy. Outdated regulations governing the grid have not kept pace with our national goals and have been a hurdle to building the grid we need.
The Benefits of Modernizing our Outdated Grid
A Stronger Economy. A more closely connected and integrated grid opens up power markets and helps to lower costs to consumers. Building new transmission that connects renewable energy projects spurs job creation up and down the supply chain. A modern grid is more reliable, resilient, and secure, not only allowing more electricity to flow through the system but helping it to do so in a smart, efficient way. With better communications and controls at all levels of this complex system, consumers will get the power they need, when they need it, and often at a lower cost.
Clean Energy. From the winds of the Great Plains and our nation’s coasts to the desert sun of the Southwest, America has vast potential to generate abundant, cheap, renewable power to revitalize our economy, strengthen our national security, reduce pollution, and mitigate climate change. In order to tap this great resource, we must expand and upgrade our high-voltage electric power transmission system so that domestic renewable energy resources stranded in our rural areas will be developed and delivered around the country.
 The Roadmap to our Energy Future
The Roadmap to our Energy Future
We all benefit from a robust and reliable transmission system, but there are crucial changes that must be made if we are to maximize the potential of a modern grid. To realize these benefits, we much change the way we plan, site, and pay for grid investments. We need a more coherent strategy that takes into account regional and national priorities.
The current state of transmission planning does not enable the multiple regional entities that control different parts of the nationwide grid to effectively communicate and coordinate about where and when transmission will be built, nor are they able to fairly share development costs.
These largely independent, though increasingly interconnected, grids must do more to communicate and coordinate with each other to not only keep the lights on, but also to plan for future system needs. We need national goals, and corresponding policy tools to plan, pay for, and site interstate transmission facilities to make the maximum amount of cost-effective, clean renewable energy available to consumers.
Learn more about how state and federal regulators are working with stakeholders to develop smarter, more streamlined ways to plan for new transmission infrastructure – and support our energy future.
A Stronger Economy
The development of regional transmission is central to unlocking the potential of our economy because it will deliver lower cost power to businesses, while also spurring growth in America’s clean energy industries. New transmission lowers costs by making energy markets more competitive through the introduction of cheaper, cleaner sources of power to consumers. When clean energy is allowed to compete, those industries will also grow and create jobs. Similar to other infrastructure investments, rebuilding our grid will also create construction jobs and economic activity in states hard hit by the economic downturn.
Businesses Need Access to Low Cost Power to Grow
When businesses have access to low cost power, they can grow and create jobs. Right now, many regions of the country have closed energy markets that only offer high cost power to businesses and residents. Regional transmission will link more businesses to competitive wholesale energy markets, and give them access to cheaper forms of energy.
New transmission projects save businesses from paying millions each year in unnecessary congestion costs.
Did you know that in the Northeast alone, congestion on the grid cost consumers and businesses $2.12 billion in 2008 – approximately 6 percent of total electricity bills? (Congestion costs in the PJM Regional Transmission Organization within the Eastern Interconnection. Department of Energy’s National Electric Transmission Congestion Study, December 2009.) These congestion costs equal the total cost of the existing transmission infrastructure as reflected in these electricity bills, but could be eliminated with a relatively modest investment in targeted incremental transmission.
Competitive markets offer choices and lower costs
The Department of Energy called the modern electric grid “the interstate highway system for wholesale electricity commerce.” Just as the interstate highway system is integral to the free flow of commerce and open markets, so too is an integrated national energy grid.
The grid’s current capacity and aging condition prevents the interconnection of new renewable energy sources. This congested and inadequate grid forces customers to pay for increasingly expensive power while keeping cleaner and cheaper alternatives out of the market. By investing in the creation of a more modern power grid, we can connect consumer to the lowest cost generation sources to meet their demands – and keep costs low.
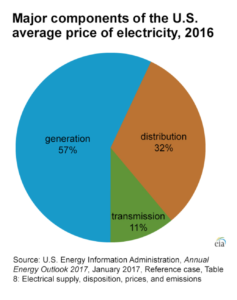
In the delivery of power to customers, there are three stages: generation at the power plant, transmission across high-voltage lines, and distribution to the end-user. Electric generation by utilities makes up more than two-thirds of an electric bill. This is the portion of a bill that would shrink with increased access to the competitive wholesale energy market. In the U.S., electricity generation makes up for 57% and distribution 32% of the average electricity price, transmission represents only 11% of what the customer pays (U.S. Energy Information Administration).
Investments in the grid will create jobs
Building a truly 21st Century electric transmission grid will create jobs. A study from the Working Group for Investment in Reliable and Economic Electric Systems (WIRES) and The Brattle Group provides compelling evidence to highlight the employment and economic benefits of investment in transmission infrastructure in the U.S. and Canada. The study finds that expanding and upgrading the grid to meet identifiable economic and reliability needs, as well as state renewable energy mandates, will help drive economic recovery and set the stage for the electric economy of the 21st century.
This analysis shows that annual investment in new electric transmission facilities could soon reach $12-$16 billion in the United States, resulting in $30-$40 billion in annual economic activity. Economic growth of this kind would support 150,000-200,000 new full-time jobs in the U.S. in each of the next 20 years. The study also predicts that investment in needed transmission will annually support 130,000-250,000 full-time U.S. jobs in the emerging renewable energy industry to which transmission capacity is so critical.
Growing Our Clean Energy Sources
Modernizing and expanding the nation’s electric grid is the key to unlocking America’s vast potential to generate clean energy from sources such as wind and solar. Expanding the grid to its current scale was one of the greatest accomplishments of the 20th century. The 21st century requires greater reliability and further electrification of our economy, but it also requires clean energy that does not contribute to climate change.
Potential renewable energy projects are languishing around the country as developers await construction of the transmission lines needed to carry power to consumers – it takes more than twice as long to build a transmission line as it does to build a wind-farm or a solar-energy array, but there is no current market path that allows transmission to go first. Current renewable sources like wind, solar and geothermal power are abundant, but our aging electricity grid doesn’t connect renewable energy-rich regions to the population centers that need it most. As of 2016, there were 136,800 MW of wind projects waiting to connect to the grid – that’s enough capacity to meet approximately 15 percent of our electricity needs.
Modernizing our grid not only gives more Americans access to diverse electricity resources and the jobs and environmental benefits they bring. A secure, flexible and robust grid enables operators to balance the flow of energy from variable renewable energy sources and enhance the reliability of our nation’s power supply. Renewable energy is not only clean, it is also affordable. Once a developer has invested the upfront capital costs, the wind, the sunshine, and the heat of the earth itself – unlike fossil fuels – are free, meaning that a renewable energy producer will always send his or her electricity output to market, regardless of the prevailing market price, thus providing a profound influence toward lower market prices.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gSiCRZcJnfE&feature=youtu.be

 The Roadmap to our Energy Future
The Roadmap to our Energy Future